The Dementia Diagnostic Unit is aimed at all those people with memory loss or other symptoms of cognitive impairment who need an accurate initial diagnosis of their process or a second opinion after a previous evaluation.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnostic process is carried out in a single act in which professionals from different specialties take part and in which the following evaluation, neuroimaging and laboratory tests necessary to reach the diagnostic conclusion are carried out in a personalized, planned and coordinated manner:
NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT
Consists of the application of a battery of tests with which the state of the main mental functions is assessed: memory, language, reasoning, calculation, reading, writing, attention, orientation, recognition, motor skills…
FUNCTIONAL ASSESSMENT
Values the ability of the person to perform the tasks necessary for self-care and to maintain their independence: eating, grooming, dressing, handling money, working, traveling…
BEHAVIORAL ASSESSMENT
Detects the presence of affective and behavioral disorders: hallucinations, delirium, anxiety, depression, irritability, aggressiveness, apathy, disinhibition, excessive motor activity, sleep disturbances and appetite…

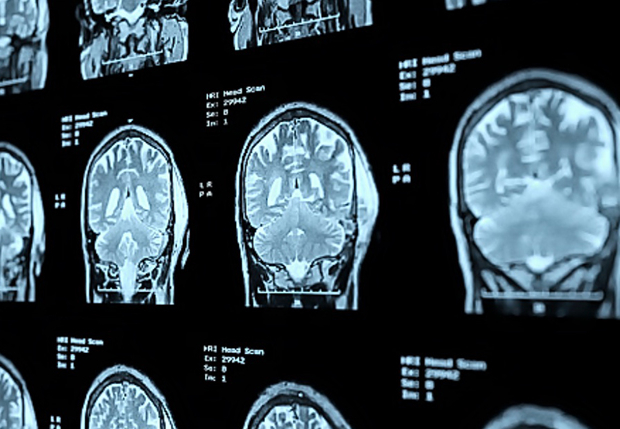
Neuroimaging test
Brain neuroimaging techniques provide a picture of the brain and have great value in making a positive diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
Depending on the particular characteristics of each case, different techniques may be used:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET).
- Single photon emission tomography (SPECT).
Laboratory tests
A general blood test is requested that includes some special data in order to rule out processes that may cause brain alterations.

Clinical report
The results of the evaluation process are recorded in writing in a diagnostic report that includes all the assessments and explorations carried out to arrive at the clinical formulation. It also contains an intervention and follow-up plan with specific and personalized recommendations aimed at both the patient and his or her relatives.
